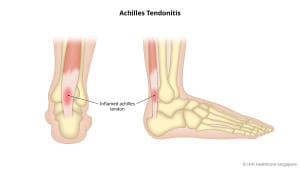
Achilles tendinitis is a condition characterised by inflammation of the Achilles tendon, which is the largest tendon in the body. It connects the calf muscles to the heel bone and is responsible for enabling movement of the foot and ankle. Achilles tendinitis typically occurs due to overuse or repetitive strain on the tendon, leading to microtears and subsequent inflammation.
Symptoms of Achilles tendinitis may include:
- Pain and stiffness along the back of the heel, particularly during physical activity or when walking or running.
- Tenderness and swelling in the affected area.
- Morning stiffness and pain that improves with mild activity.
- Thickening of the Achilles tendon.
- Limited range of motion in the ankle.
If you suspect you have Achilles tendinitis, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and guidance on treatment options. One of our experienced physiotherapists will perform a physical examination, review your medical history, and potentially recommend additional tests such as an ultrasound or MRI to assess the severity of the condition.
How is it treated?
Treatment for Achilles tendinitis typically involves a combination of conservative measures aimed at reducing pain and inflammation, promoting healing, and preventing further injury.
Some common treatment approaches include:
- Relative rest: Avoid activities that exacerbate the pain. This may involve temporarily reducing or modifying your physical activity level.
- Isometric exercises: Whilst rest from aggravating activities is important, complete rest is actually counterproductive. In order to promote tendon healing, you need to commence a tendon rehabilitation program which begins with static hold exercises called “isometric exercises”.
- Correction of movement mechanics: Strength and alignment exercises to improve movement technique and postural alignment to reduce problematic forces on the achilles tendon.
- Hands-on physiotherapy: massage and joint mobilisations to improve flexibility of the muscles, connective tissues and joints that impact the achilles tendon.
- Orthotic devices: Shoe inserts or orthotic devices can provide support and cushioning to the heel and reduce stress on the Achilles tendon.
- Footwear modifications: Wearing appropriate footwear, such as shoes with proper arch support and a cushioned heel, can help relieve strain on the Achilles tendon.
If left untreated, acute Achilles tendinitis can progress into chronic tendinopathy (breakdown in the quality of tendon tissue from overload), which can then progress to tendon tearing. It is therefore imperative to correctly treat and manage Achilles tendinitis early in order to prevent injury progression.
Note: the information provided here is for general knowledge, and it’s always best to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan tailored to your specific situation. If you are suffering from pain in the Achilles or heel, come in and see one of our physiotherapist’s today for a thorough assessment and treatment plan!